Teething
Concerns
- Teething does not cause fever, upper respiratory infection, ear infection, or diarrhea.
- Teething may cause fussiness.
- Drooling is developmentally normal in infancy.
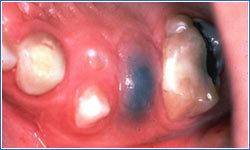
Eruption Hematoma
Anticipatory Guidance
- Apply cold teething ring or cloth to gums.
- Provide acetaminophen or ibuprofen if necessary.
- Avoid teething gels—they are not effective and contain topical anesthetics (benzocaine) which can be dangerous in infancy. The FDA warned in 2018 that over-the-counter drug products containing benzocaine should not be used to treat infants and children younger than 2 years. Such products carry serious risks and provide little to no benefits for treating oral pain. Benzocaine can cause a condition in which the amount of oxygen carried through the blood is greatly reduced (methemoglobinemia) which can be life-threatening or lethal.
- Remember tooth emergence may be preceded by a hematoma—no treatment is needed in primary dentition.
- Recommend never to dip pacifier in honey or other sweetened food.
References
Pereira TS, da Silva CA, Quirino ECS, Xavier Junior GF, Takeshita EM, Oliveira LB, De Luca Canto G, Massignan C. Parental beliefs in and attitudes toward teething signs and symptoms: A systematic review. Int J Paediatr Dent. 2023; 33(6):577-584.
Sood S, Sood M. Teething: myths and facts. J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2010. 35(1): 9-13.
U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Drug Safety Communications. Risk of serious and potentially fatal blood disorder prompts FDA action on oral over-the-counter benzocaine products used for teething and mouth pain and prescription local anesthetics. 5-23-2018. View site here.