Xerostomia
Iatrogenic is the term for adverse effects caused by diagnostic and therapeutic interventions.
Xerostomia
Saliva rinses the mouth and cleans the teeth between meals, neutralizing acids produced by bacteria and allowing the teeth to remineralize. Decreased saliva flow results in dry mouth (xerostomia), which promotes caries and periodontal disease.
Commonly prescribed medications produce xerostomia, including:
- Steroids (e.g., prednisone)
- Antihistamines (e.g., diphenhydramine)
- Diuretics (e.g., furosemide)
- Antihypertensives (e.g., beta-blockers)
- Opioids (e.g., codeine)
- Antidepressants (e.g., Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors and lithium)
Many medications can contribute to xerostomia, and patients who take multiple medications are at highest risk. As a health care professional, ensure that medications that can induce xerostomia are critical to a patient's oral and overall health.
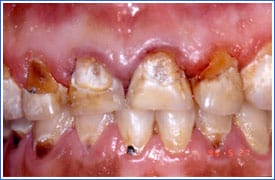
Severe Adult Caries
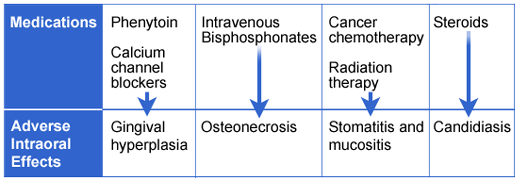
Many additional classes of medications can have adverse intraoral effects:
References
Wolff A, Joshi RK, Ekström J, et al. A Guide to Medications Inducing Salivary Gland Dysfunction, Xerostomia, and Subjective Sialorrhea: A Systematic Review Sponsored by the World Workshop on Oral Medicine VI. Drugs R D. 2017; 17(1): 1-28.