Social Determinants of Oral Health
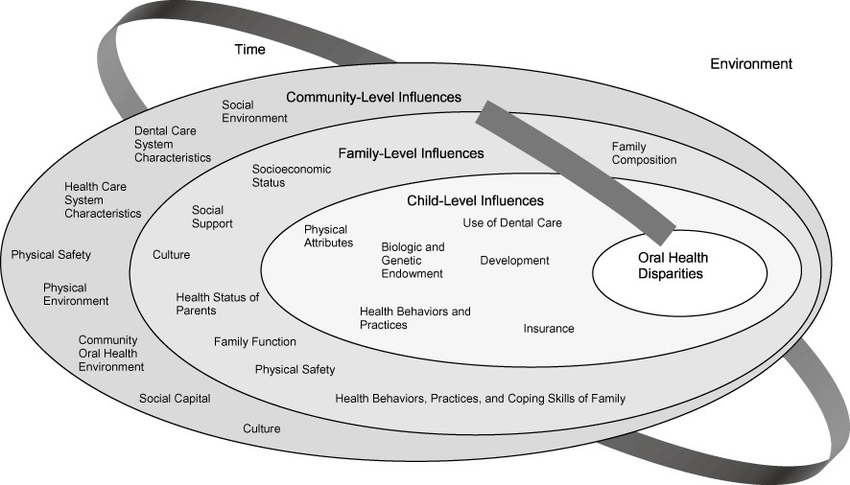
The child, family, and community all influence the oral health outcomes of children.
- Oral health inequities are largely influenced by community level rather than individual factors
- Integrated approach of policy and individual influences promote the greatest impact on health inequities, including oral health
- Health care teams have a critical role in promoting oral health equity for patients and communities. Primary care teams are well positioned to promote oral health during routine well child visits, but also medical-dental integration within the wider community.
Child level influences include:
- Physical attributes, biologic and genetic characteristics
- Health behavior and practices
- Dental insurances and use of dental care
Family level influences include:
- Family culture, function, and composition
- Socioeconomic status, social supports, safety
- Health behaviors, practices, and coping skills; parent health status
Community level influences include:
- Social environment and social capital
- Characteristics of the dental and health care systems
- General culture and oral health environment
- Physical environment and safety
References
Susan A. Fisher-Owens, SA Gansky, LJ Platt, et al. Influences on children's oral health: A conceptual model. Pediatrics 2007; 120(3): e510.
Watt RG, Sheiham A. Integrating the common risk factor approach into a social determinants framework. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. 2012; 40: 289–296.
Social Determinants of Health: A Quick Guide for Health Professionals. Julie Mikkonen and Dennis Raphael, 2012.
Luo H, Wu B, Wu Y, Moss ME. Dental Caries and Preventive Dental Visits Among Children in the U.S.: The Impact of Race/Ethnicity and Immigration. AJPM Focus. 2024; 19;3(4):100230.
Pierce A, Singh S, Lee J, Grant C, Cruz de Jesus V, Schroth RJ. The Burden of Early Childhood Caries in Canadian Children and Associated Risk Factors. Front Public Health. 2019 Nov 12;7: 328.
Cortés DE, Réategui-Sharpe L, Spiro Iii A, García RI. Factors affecting children's oral health: perceptions among Latino parents. J Public Health Dent. 2012; 72(1):82-9.
The triad was adapted from Keyes PH. Int Dent J. 1962;12: 443–464; and the concentric oval design was adapted from the National Committee on Vital and Health Statistics. Shaping a Health Statistics Vision for the 21st Century. Washington, DC: Department of Health and Human Services Data Council, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics; 2002:viii.
Figure published in Pediatrics by: Fisher-Owens SA, Gansky SA, Platt LJ, et al. Influences on children's oral health: A conceptual model. Pediatrics. 2007;120(3); e510.
Figure above adapted from the following 2 sources, with secondary, explicit permission obtained for use in the Smiles for Life Curriculum:
- Keyes, PH. Recent advances in dental research: bacteriology. (1962). Int Dent J; 12:443-464. Permission granted by Wiley Publication for use of the caries triad concept. Reference is: Keyes, P.H. Recent advances in dental research: bacteriology. Int Dent J 1962; 12:443-464. Reprinted with permission of John Wiley & Sons, Inc.
- Concentric Oval Design adapted, with permission, from Shaping a Health Statistics Vision for the 21st Century. Figure 1. Influences on the Population's Health. Washington, DC: Department of Health and Human Services Data Council, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics; 2002:viii.