Pediatric Oral Exam
Oral exams should be performed at each well child visit, with formal risk assessment starting at 6 months of age.
Procedure
- Lift the lip
- Look at all the teeth—front, back, and sides
- Note plaque, white spots, cavities, abscesses, and damaged teeth
- Examine the soft tissues- including the tongue, lips, gums and cheeks
- Palpate the palate to rule out submucosal clefts
Small children are best examined while lying down. For infants and toddlers, the knee-to-knee oral examination allows you to carefully examine the child's teeth with assistance from a caregiver. If the child's legs do not fit around the caregiver's body, the child may lie sideways or diagonally on the caregiver's lap.
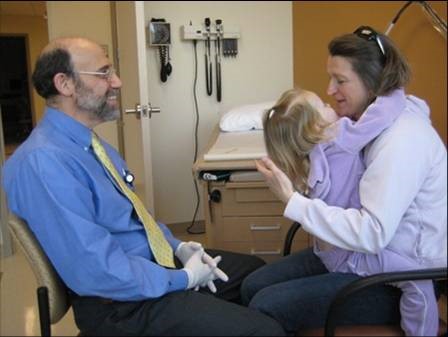
Step 1
Child is held facing caregiver in a straddle position
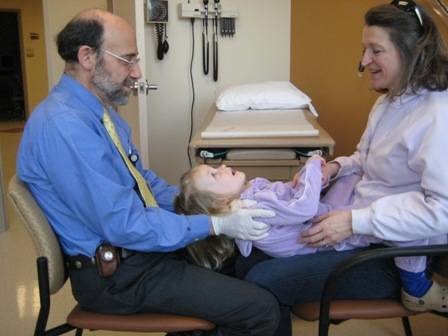
Step 2
Child leans back onto examiner's lap while caregiver holds child's hands
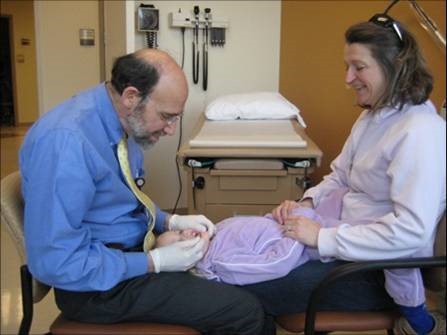
Step 3
Provider performs exam while caregiver holds child's hands and legs
For detailed info about the oral exam, including differences between primary and permanent teeth, see Smiles for Life Oral Examination module.