Dental Caries
Dental caries is the most common chronic disease of childhood from ages 6 to 19.
Dental caries is largely preventable.
Caries destroy tooth structure leading to infection, pain, and loss of chewing function.
Early Childhood Caries is an aggressive form of caries in children under 6 years of age. ECC was once called "nursing caries" or "baby bottle tooth decay."
Etiology
- Influenced by socioeconomic status, feeding habits, access to dental care, fluoride exposure, and family caries experience.
Progression of ECC
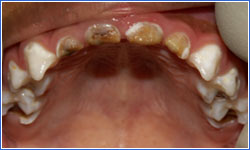
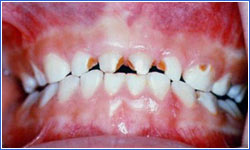
- Upper front teeth (incisors) that are least protected by saliva are affected first.
- Disease moves posteriorly as teeth emerge.
Severe Early Childhood Caries
References
Policy on Early Childhood Caries (ECC): Classifications, Consequences, and Preventive Strategies. American Academy of Pediatric Dentistry Council on Clinical Affairs. 2016. 59-61.
www.cdc.gov/healthywater/hygiene/disease/dental_caries.html